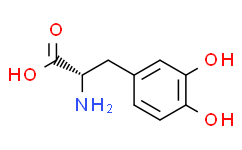
左旋多巴抑制劑Levodopa?is an amino acid precursor of?dopamine?with antiparkinsonian properties.?Levodopa?is a prodrug that is converted to?dopamine?by?DOPA?decarboxylase and can cross the blood-brain barrier. When in the brain,?levodopa?is decarboxylated to?dopamine?and stimulates the dopaminergic receptors, thereby compensating for the depleted supply of endogenous?dopamine?seen in Parkinson's disease. To assure that adequate concentrations of?levodopa?reach the central nervous system, it is administered with?carbidopa, a decarboxylase inhibitor that does not cross the blood-brain barrier, thereby diminishing the decarboxylation and inactivation of?levodopa?in peripheral tissues and increasing the delivery of?dopamine?to the CNS.